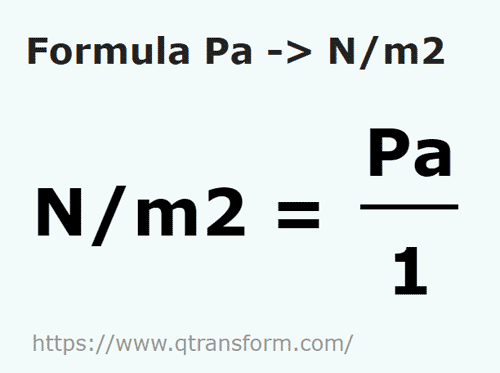SOLVED: The volume of an ideal gas is increased from 0.39 m3 to 3.6 m3 while maintaining a constant pressure of 1141 Pa (1 Pa = 1 N/m2). If the initial temperature

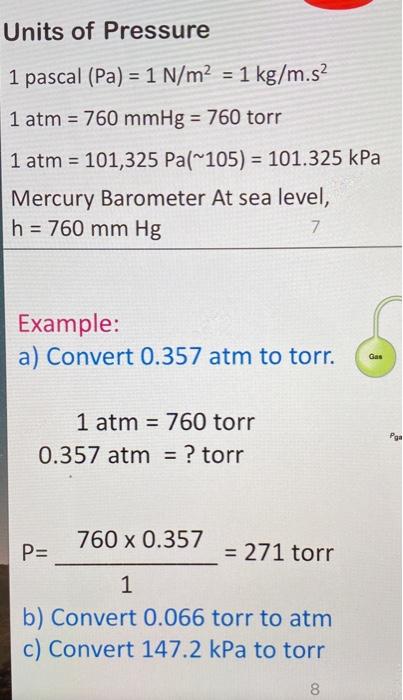
The pressure required to reduce the given volume of water by 1% is, (Bulk modulus of water =2xx10^(9)N//m^(2))

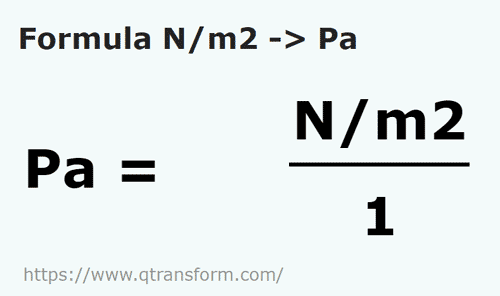
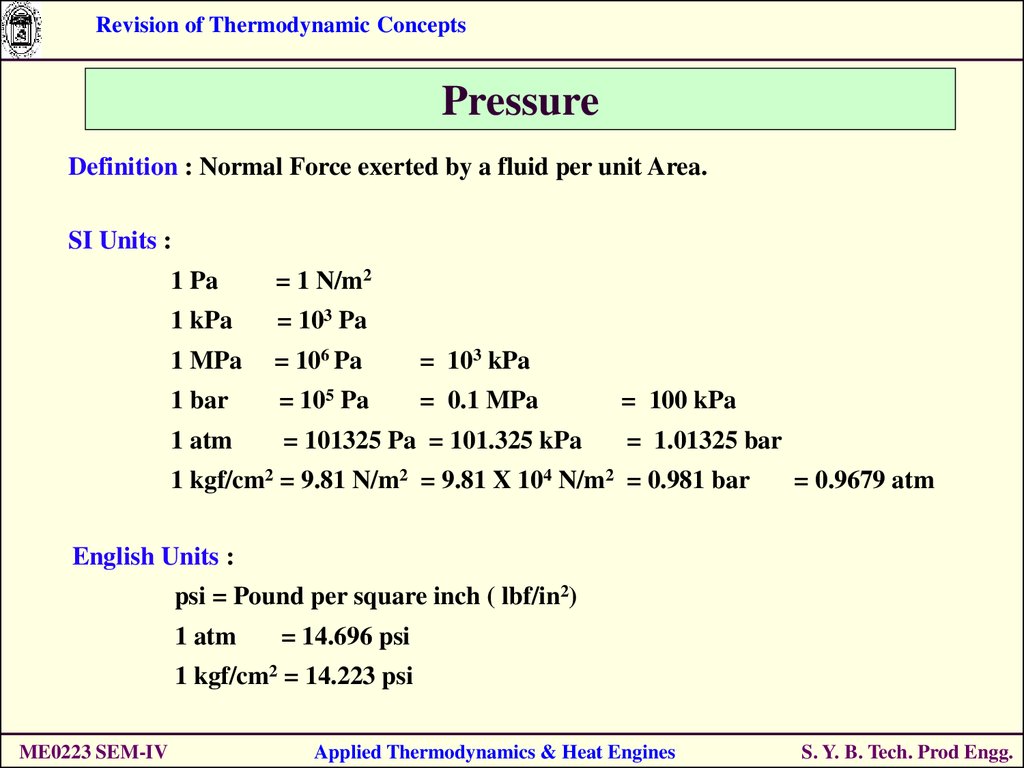
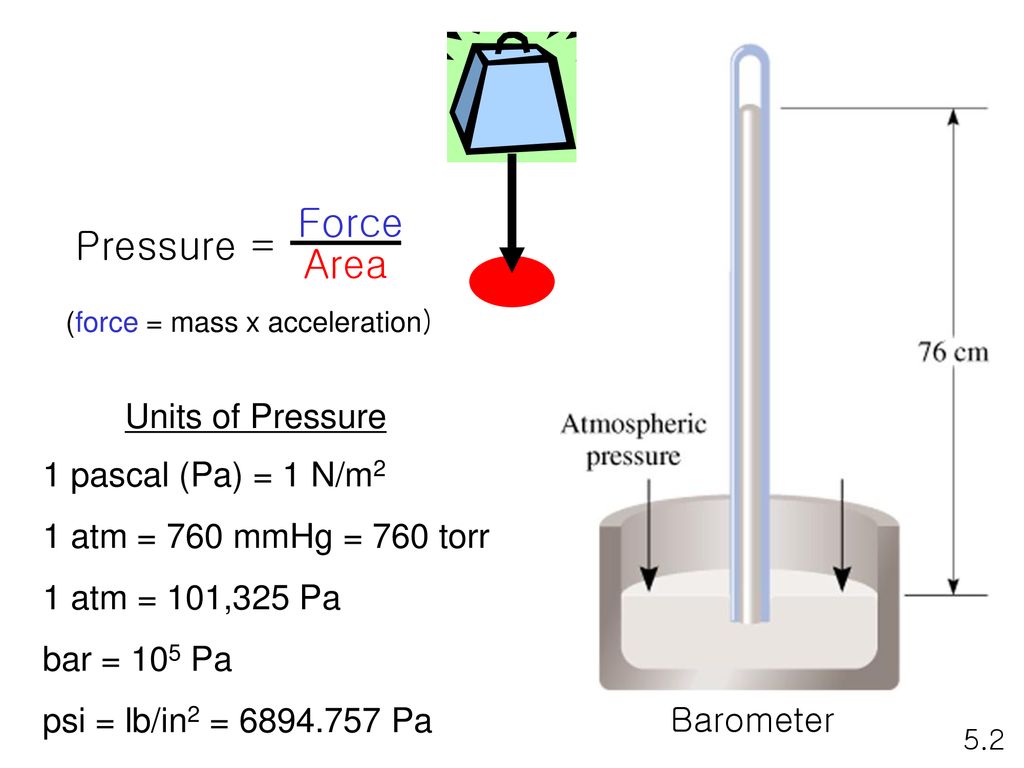
SOLVED: A Pascal (Pa) is defined as the pressure exerted by force of Newton (N) acting on an area of one square meter (1Pa IN/m^2). A Newton is represented by the follwoing
1 1–1. Round off the following numbers to three significant figures: (a) 4.65735 m, (b) 55.578 s, (c) 4555 N, and (d) 2768 kg.

The hand pushed the lever down with a force of F in the drawn picture. The area at (1) of the pipe inside the fluid system is 1 cm2 and the area

Unit conversion of Pascal | Pascal to N/m2 | How to convert kpa to N/m2|How to convert Mpa to N/mm2 - YouTube