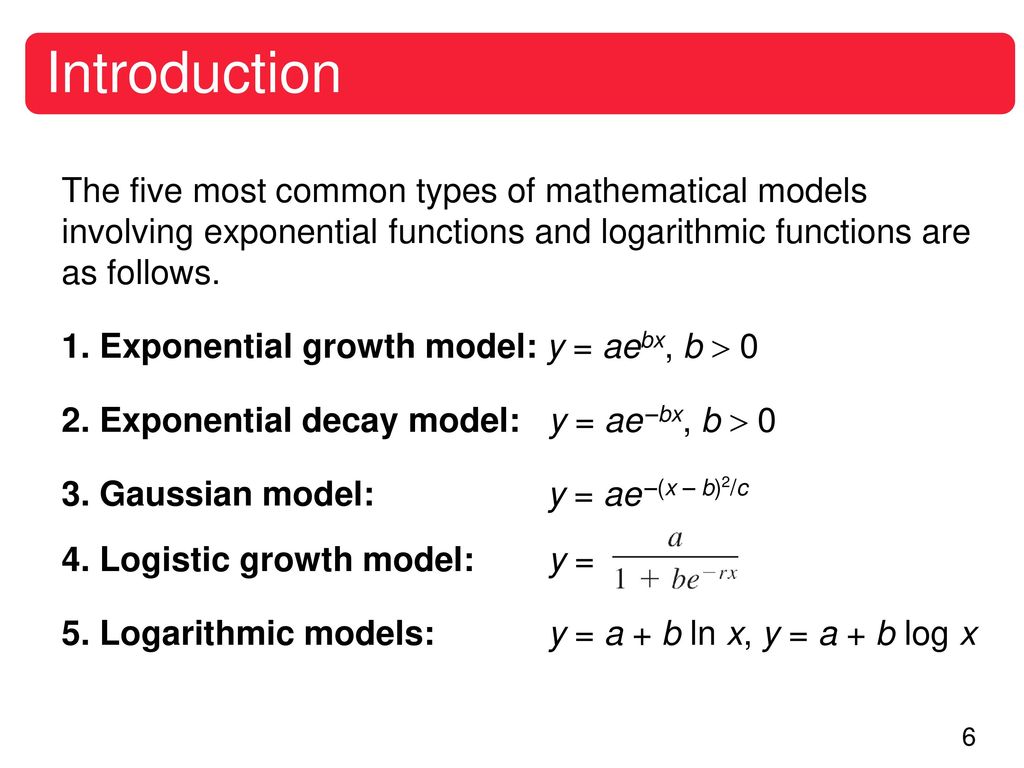
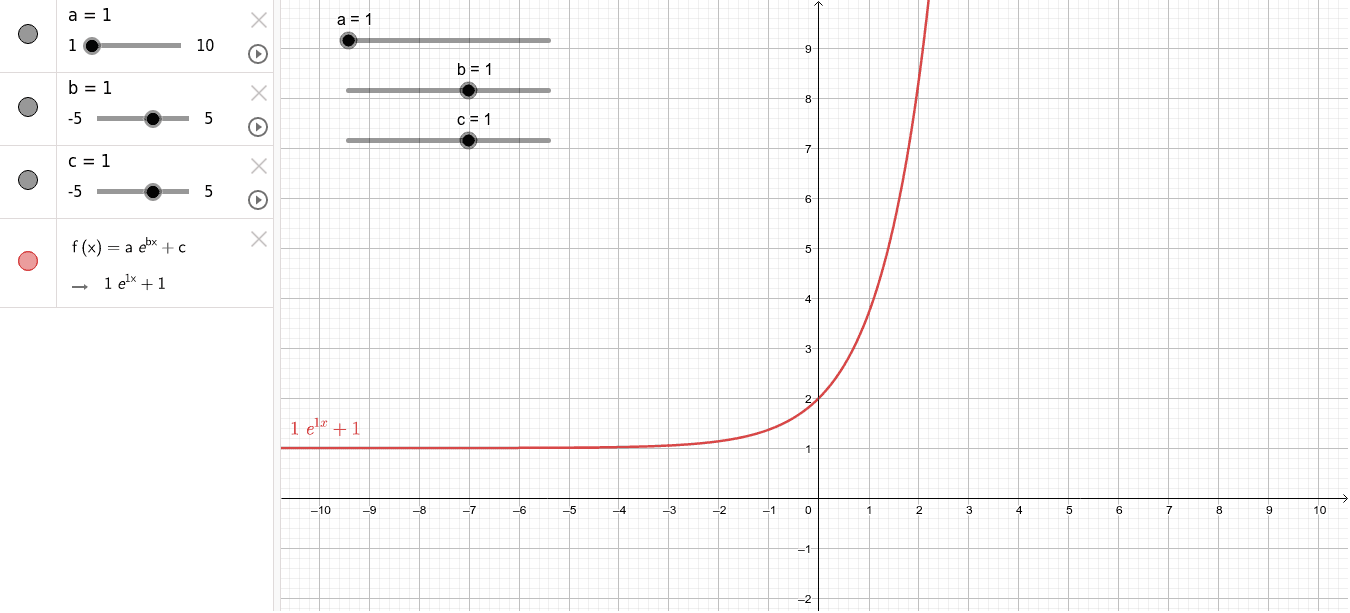
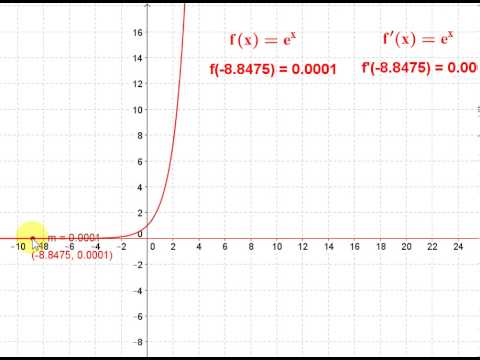
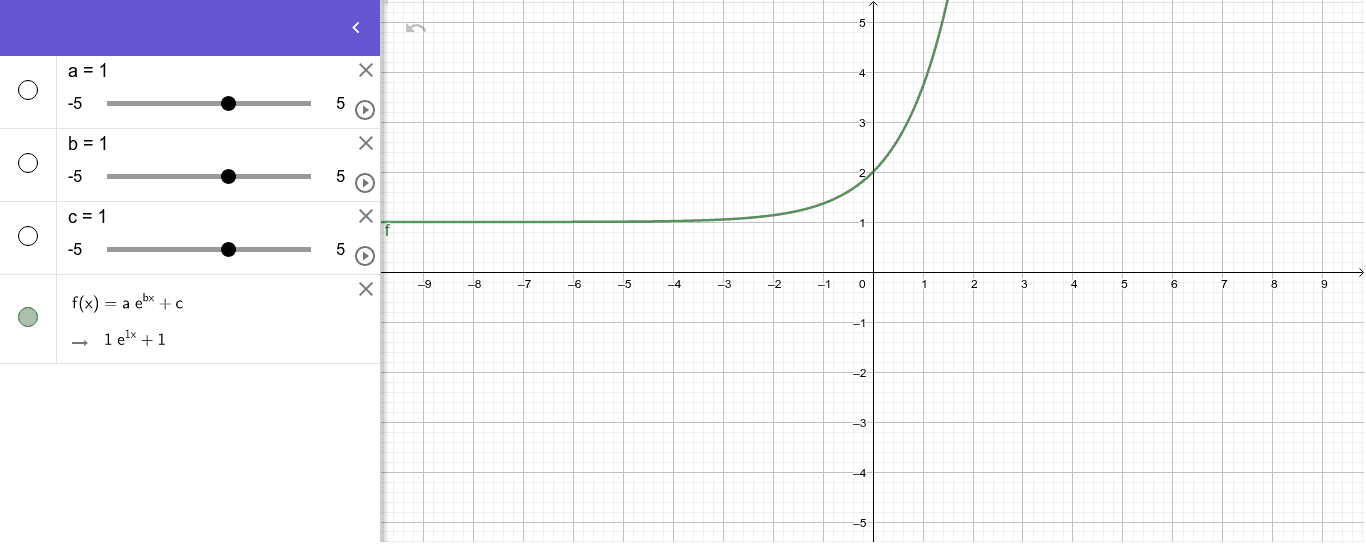
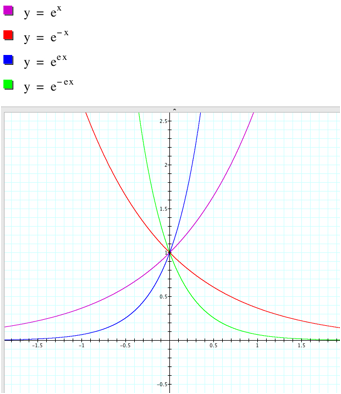
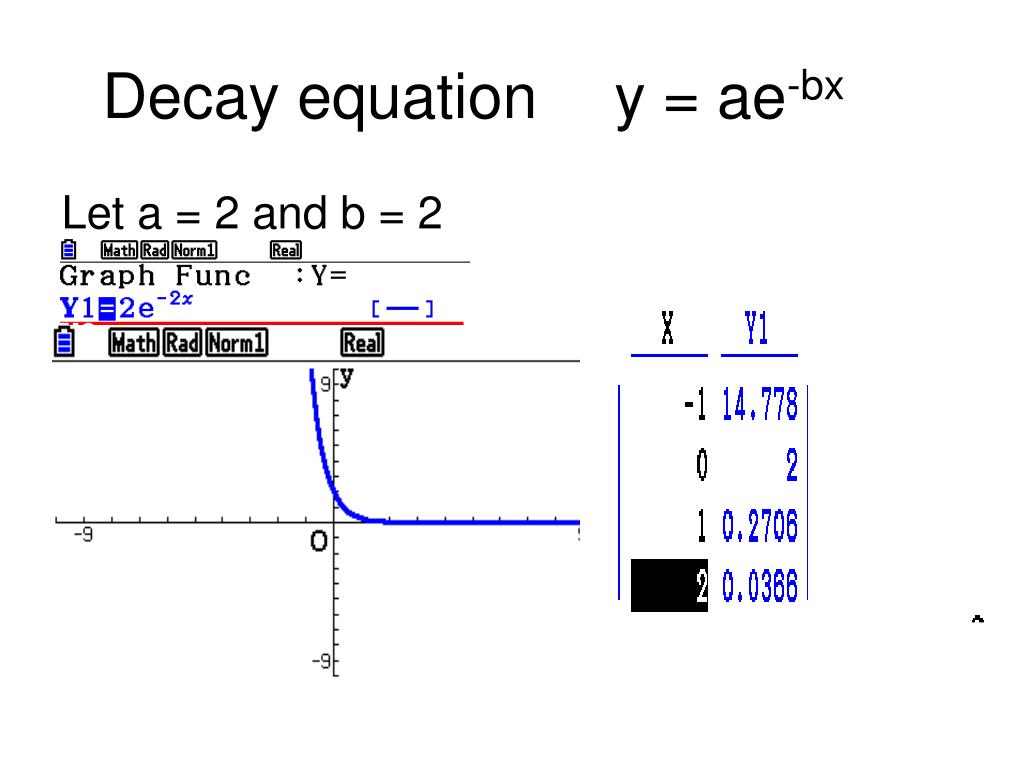
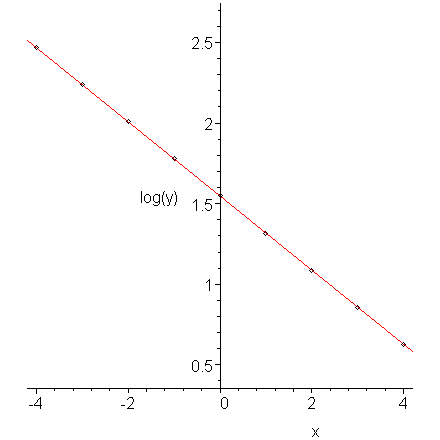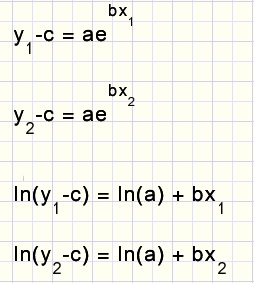Verify that y = ae^(bx) is a solution of the differential equation (d^2y/dx^2)=1/y(dy/dx)^2 - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

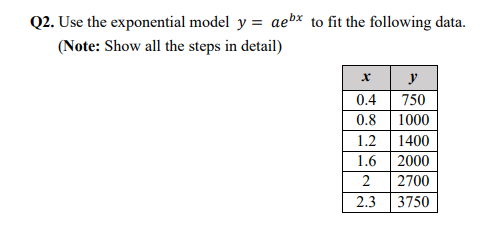
SOLVED: Q2: Determine the constants a and b by the method of least squares such that bx y =a e fits the following data: 2 10 y 4.077 11.084 30.128 81.897 222.62
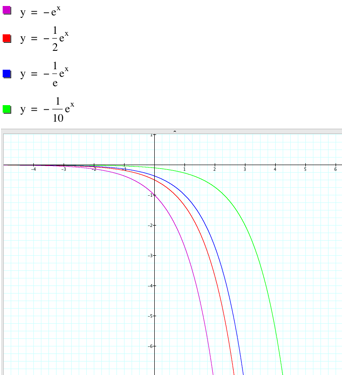
Find the differential equation representing the family of curves y = a e^bx+5, where a and b are arbitrary constants. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

P&S-CURVE FITTING-Problem on to fit a curve of exponential y=ae^bx by least squares method-class8 - YouTube