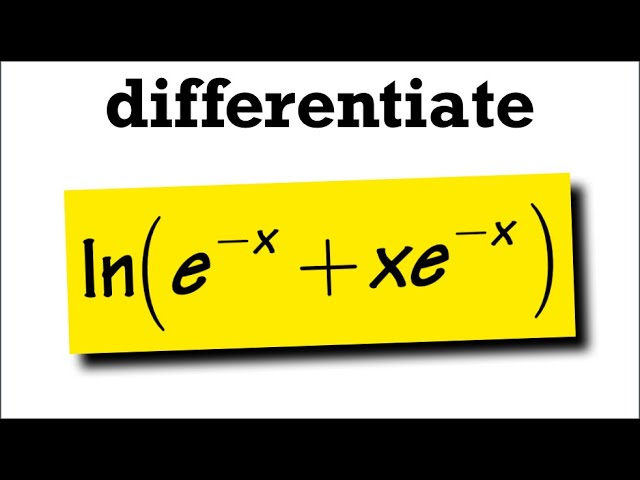
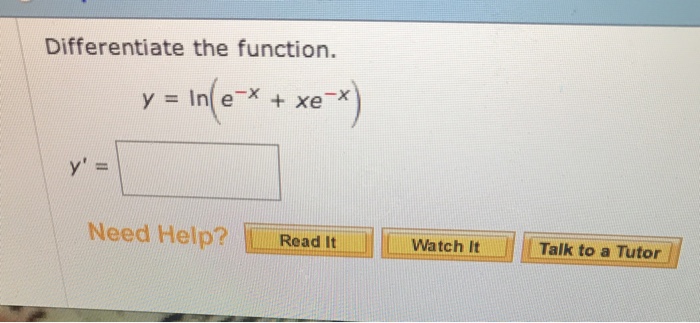
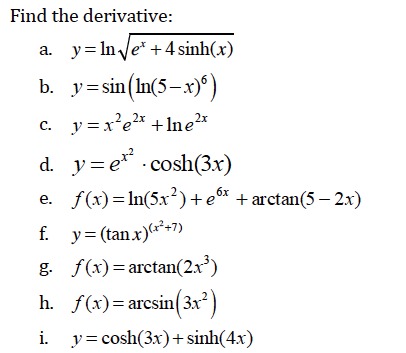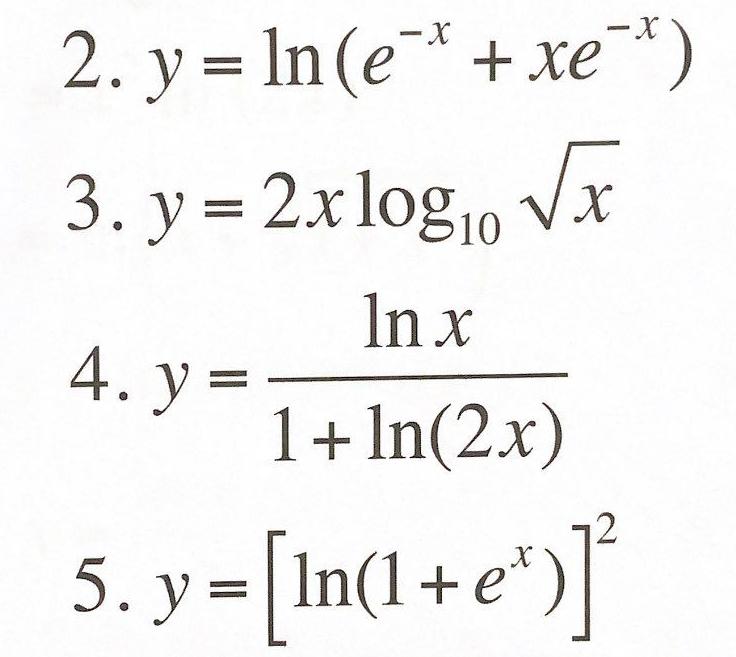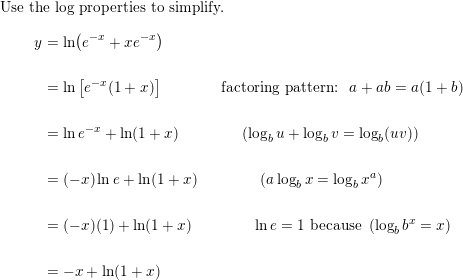integration - How to find the area bounded by $y=\ln\left(x\right)$ and $y=e+1-x$, and the $x$ axis? - Mathematics Stack Exchange

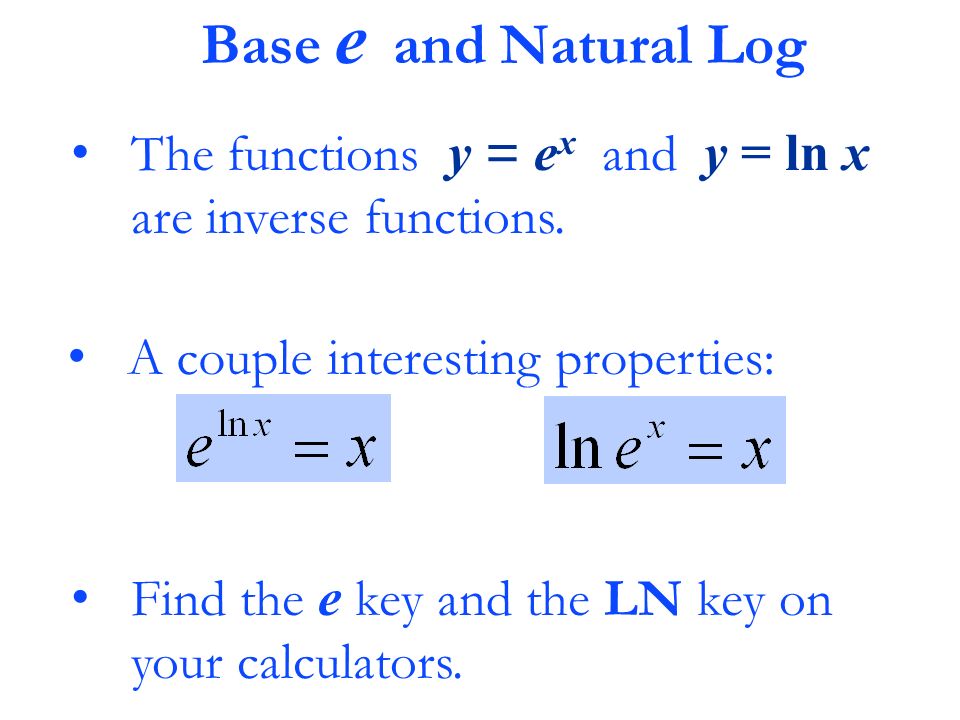
E/ Natural Log. e y = a x Many formulas in calculus are greatly simplified if we use a base a such that the slope of the tangent line at y =

Find the slope of the graph of y = ((ln x)^4)/x at the point (e, 1/e). Slope is ___. Now find an equation for the tangent line at that point, then solve

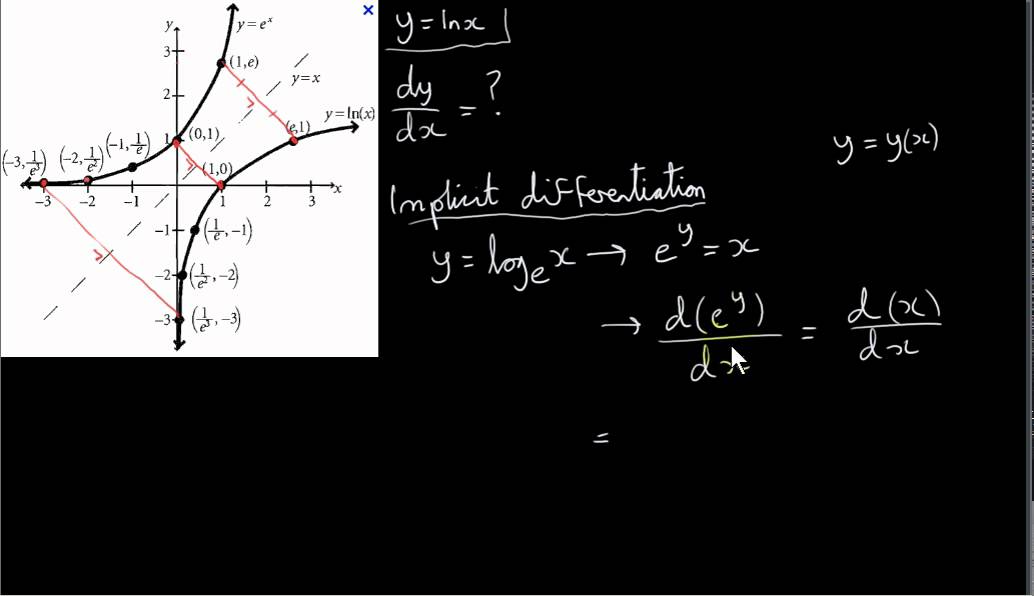
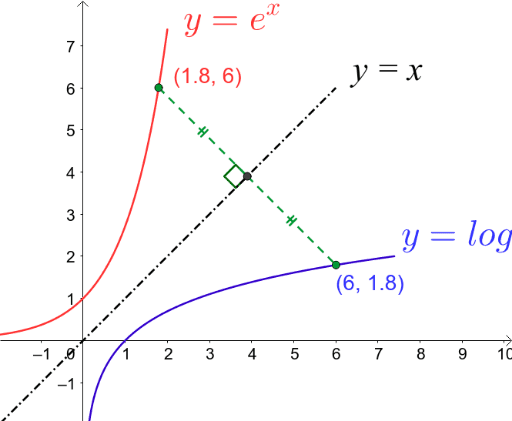
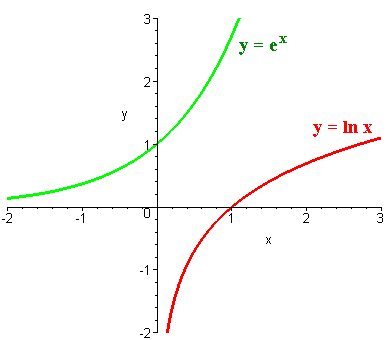
Describe the graphs of y = e^x and y = ln x. Relate one graph with the other and describe that relationship. | Homework.Study.com

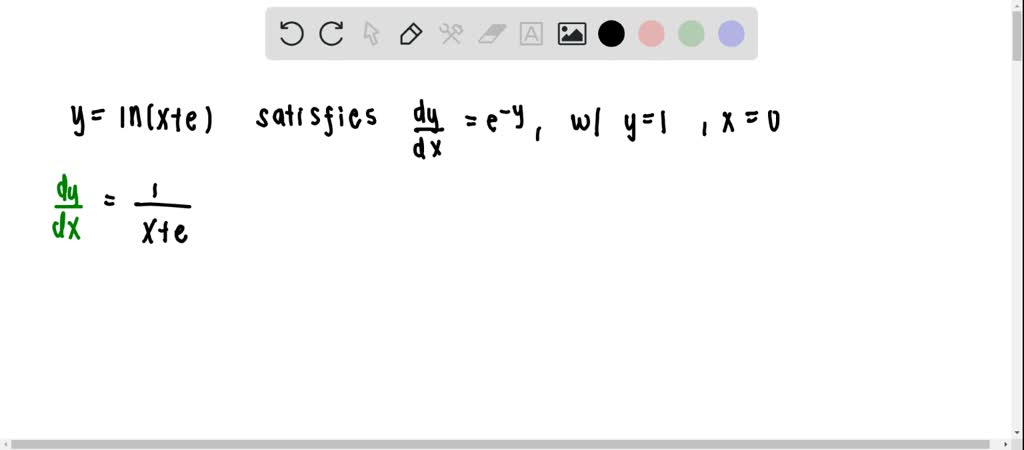
ordinary differential equations - How does $ln(y) = 2x+C$ become $y = e^{2x+C}$? - Mathematics Stack Exchange